Dog Pregnancy Calculator And Timeline
Indeed, Cocker Spaniel is one of the interesting old dog breeds that we must know about! Cocker Spaniel dogs originate from Spain where the term Spaniel is a French word that means Spanish.
There are two recognized Cocker Spaniel breeds: the English Cocker Spaniel (recognized by the English Kennel Club) and American Cocker Spaniel (recognized by the American Kennel Club).
The initial purpose of breeding this dog breed was to utilize its services during hunting.
Cocker Spaniel Breed Characteristics
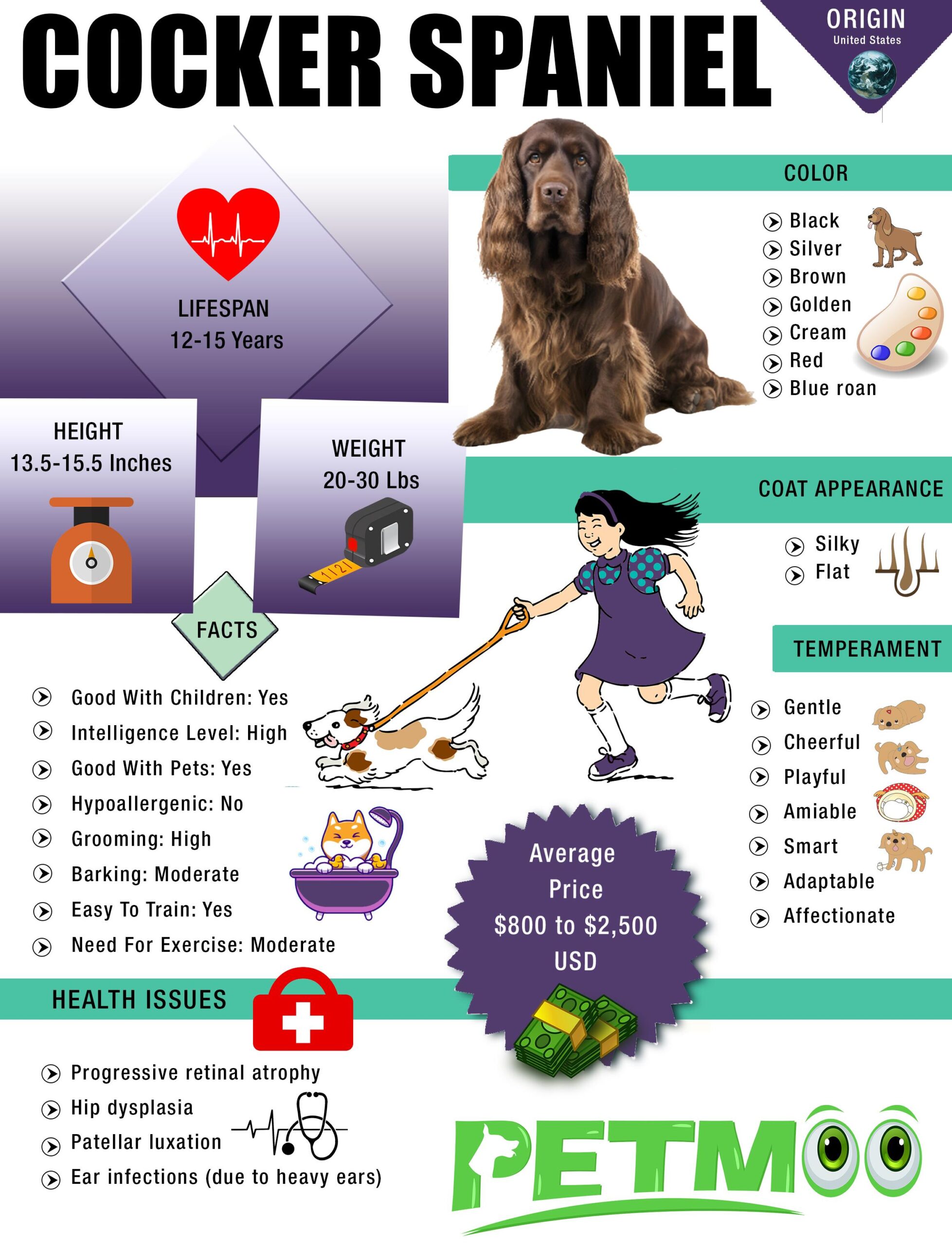
- Origin: United States (American Cocker Spaniel), United Kingdom (English Cocker Spaniel)
- Size: Small to Medium
- Dog Breed Group: Sporting Group
- Purebred: Yes
- Lifespan: 12-15 Years
- Height: 13.5-15.5 inches (34-39 cm)
- Weight: 20-30 pounds (9-14 kg)
- Coat Appearance: Silky, flat or slightly wavy
- Coat Colors: Black, silver, brown, golden, cream, red, blue roan, various patterns and markings
- Temperament: Gentle, affectionate, cheerful, playful, amiable, smart, adaptable
- Good With Children: Yes
- Intelligence Level: High
- Good With Pets: Yes
- Hypoallergenic: No
- Grooming: High
- Barking: Moderate, more when they feel necessary
- Suitable For Apartments: Yes, if exercised properly
- Need For Exercise: Moderate
- Easy To Train: Yes, generally eager to please
- Good For First Time Owners: Yes, they are friendly and trainable which makes them good for novice owners
- Health Issues: Progressive retinal atrophy, hip dysplasia, patellar luxation, ear infections (due to heavy ears)
- Litter Size: 3-7 puppies
- Average Price: $800 to $2,500 USD
Cocker Spaniel Facts
Coat Color
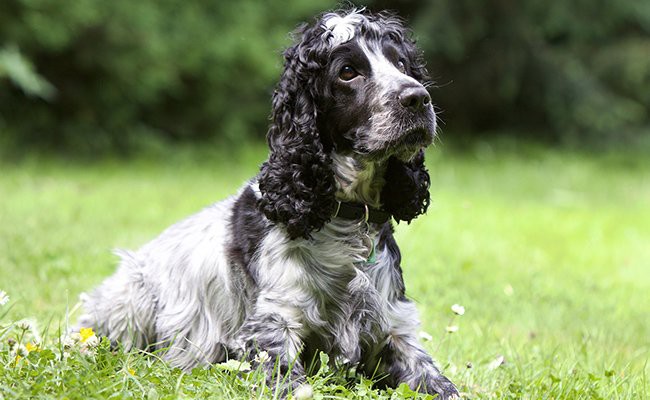
The Cocker Spaniel can appear in a variety of colors such as Black, Black & Tan, Black and White, Orange Roan, Orange & White, Lemon & White, Liver Roan, Liver, Liver and Tan, Blue Roan and Ash.
Cocker Spaniel Appearance
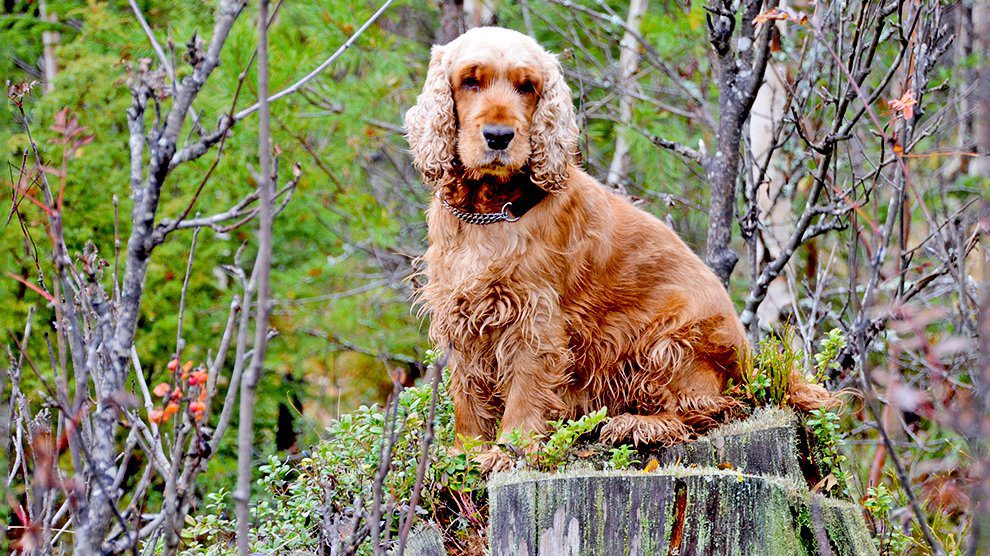
The smallest member of the sporting dog group, Cocker Spaniel is a well balanced stocky-built dog with a compact body. The dog has a chiseled and refined head that is round and also graceful in appearance.
Cocker Spaniel dog has dark big eyes and feathered long ears. The dog has a deep chest and a broad square muzzle. They have a docked tail. Cocker Spaniel dogs have a silky coat with feathering on the ears, legs, chest, and underside.
Cocker Spaniel Size
The height of a male cocker spaniel dog is 15 inches and the body weight is 13 kg. On the other hand, the height of a female cocker spaniel dog is 14 inches and the weight is 11 kg.
Cocker Spaniel Temperament
- Gentle
- Intelligent
- Adaptable
- Playful
- Trainable
- Affectionate
- Sensitive
- Friendly
- Sociable
- Loyal
Cocker Spaniel Lifespan
The lifespan of a Cocker Spaniel dog is 12 to 15 years. It is quite possible that some dogs might live even a couple of years more.
The key determinants of the life span of a Cocker Spaniel dog are its diet and the nature of the living environment in which it is raised.
A trainer/breeder/owner of a Cocker Spaniel must take utmost care of these two factors to ensure that the dog survives until the stated age range. Smaller cocker spaniel dogs live longer than the bigger ones.
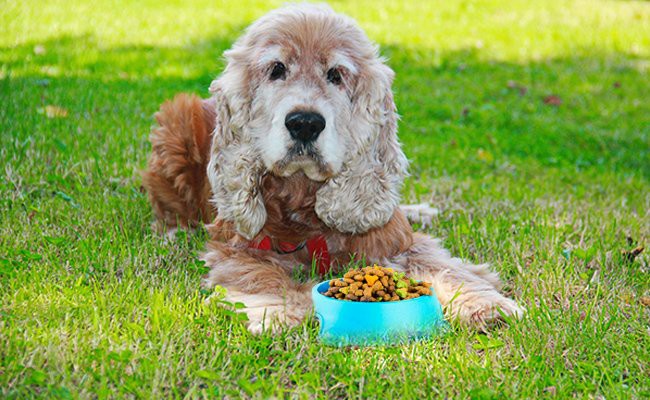
Cocker Spaniel Foods
Foods consumed by a Cocker Spaniel Dog
- High-quality brand Dry Kibble
- Duck
- Fish
- Whole Chicken
- Turkey
- Salmon
- Beef
- Lamb
- Brown Rice
- Fruits like Apples, Oranges, Bananas,
- Vegetables like Sweet Potatoes, Carrot, Lettuce, Spinach leaves, and Broccoli
Foods to “Avoid”
Cocker Spaniel Interesting Facts
- Spaniel dogs have been bred from the 1400s itself where the primary purpose was to use it as a hunting dog.
- During the 1930s and 1950s, Cocker Spaniels were the most popular dogs in the USA.
- After World War II, the Cocker Spaniel dogs started to become popular.
- Although being bred as a hunting dog, Cocker Spaniels can work on wet and dry areas.
- The name Cocker comes from the name of a bird called Woodcock, a game bird that was hunted by the Spaniel.
- There are two kinds of spaniel dogs, American Cocker Spaniel and English Cocker Spaniel.
- It is only from the English Cocker Spaniel, that the American Cocker Spaniel existed.
- According to the American Kennel Club (AKC), the American Cocker Spaniel is the smallest sporting dog.
- Celebrities who own/owned a Cocker Spaniel dog include:
Richard Nixon – Former USA President
Bill Clinton – Former USA President
Oprah Winfrey – American television Talk Show Host and Actress
Dog Names For Your Cocker Spaniel
| Male Dogs | Female Dogs |
|---|---|
| Buddy | Coco |
| Charlie | Lulu |
| Jackson | Jasmine |
| Murphy | Diamond |
| Oliver | Sugar |
| Harrison | Zara |
| Sam | Jessie |
| Sandy | Molly |
| Tyson | Sophie |
| Newton | Gracie |
| Kimba | Jade |
| Mango | Roxy |
What Are Girl Dog Names For Cocker Spaniels?
- Aggie
- Brianna
- Ellie
- Tia
- Papina
- Osito
- Ukita
- Yelena
- Wendy
- Zara
- Xalapa
- Simba
- Ushki
- Viva
- Quincy
Cocker Spaniel Health Problem
The major health problems that affect the Cocker Spaniel Dogs include:
1. Cataracts

Symptoms
- Whitish cloudy appearance on the surface of the eye
- Bluish grey haze on the pup
- Eye Irritation or reddish eyes
- Scratching of the eyes at short intervals
- Unwilling to do the usual activities of climbing stairs and jumping on furniture
- High intake of water and frequent urination for dogs with diabetes
- Loss or decrease in vision leads to:
- Unsteady walk
- Bumping on or tripping over objects
- Walking into walls
- Unable to see people
Causes
- Congenital (during birth ) due to genetic problems
- Diabetes
- Old Age
- Trauma or Injury to the Eye
- Lack of amino acids
- Free radicals
Treatment
Older dogs are always at very high risk of developing cataracts than the younger ones. Normally, a vet will do a complete physical examination of the dog, eye examination and study its disease history.
Some other eye-related tests will also be performed. Apart from this, the vet will find the treatment requirements for the dog and recommend the needful procedures like:
Recommend the dog for further treatment by a veterinary ophthalmologist, who will instruct the owner of the dog to take some tests for the dog. The purpose is to find out the main cause of cataract. The tests include:
- Chemistry tests – Done to assess the functions of kidney, liver, pancreas and to check the blood sugar levels.
- Complete blood count – To notify if there is the presence of infection, anemia, inflammation and other conditions.
- Specialty tests – Includes culture test, polymerase chain reaction test and other tests like to check whether the retina functions properly
The key factors that are considered important for the treatment of the cataract in your dog will be the basic cause, stage of the disease and the dog’s overall health condition.
The nature of treatment might be:
- To treat the fundamental cause for the occurrence of cataract, if findable
- Applying eye drops to avoid inflammation and certain secondary-level problems
- Only after checking the age and health of the dog, the veterinary ophthalmologist will operate the cataract and remove it.
2. Glaucoma

Symptoms
- Differing size of pupils in both the eyes
- Reddish eyes
- Cloudiness in the cornea
- Shaky eyelids
- Moderate to severe eye pain for the dog due to rubbing of the eye on the floor or with paw
- Squinting
- Stay away from light
- Tearing
- Lethargic response
- Slow/non-response of pupils to light
- Loss of appetite
- Aggressive Behavior
- Swollen Eye
- Defective vision leading to bumping into objects and difficulty in finding things like toys
Causes
- Genetic Factor
- Infection
- Injury
- Inflammation
- Tumour
- Luxation of lens
Treatment
Based on the stage of the disease, the needful treatment will be given by a veterinarian doctor.
The treatments comprise of:
- Medications
- Topical ointments or drops to reduce the pressure in the eyes and also decreases the level of inflammation or infection. The ointments or drops are to be applied at least 2-3 times in a day for the stipulated period given by a vet to ensure the path to recovery.
- Oral medications (tablets)
- Carbonic anhydrase inhibitor diuretics for reducing the production of fluid
- Beta blockers will be applied to lessen the production of fluid
- Give Cholinesterase inhibitors to postpone the occurrence of glaucoma in the unaffected eye
- Corticosteroids will keep inflammation under control
- Mitotic drugs will shrink the pupil for permitting the release of fluid
- Prostaglandin analog to be applied for more fluid flow from the eyes
- Osmotic diuretics are used for dehydrating the eye
- Surgical Treatment
- Cyclophotocoagulation – The laser instrument that removes the secretory epithelium, which triggers the production of fluids within the eye
- Gonioimplantation – Installing a small tube so that the fluid gets an outlet to release
- Enucleation – Entire removal of the eyeball. The surgery is undertaken only as a last resort when other treatments do not yield good results
3. Patellar Luxation
Symptoms
- Limping with one leg
- Inability to bend the knees
- Abnormal movement of the legs while walking
- Avoidance of running or jumping
- Show unwillingness to do exercises
- Pain at the time of moving the leg and will cry out for some time
Causes
- Congenital reasons (at the time of birth)
- Injury or accident which damages the bones or knee ligaments
- Weakness in the ligaments or the bones in the knee which develops over time and it can be due to a genetic (hereditary) issue
Treatment
Based on the stage of the disease, the veterinarian will decide on the course of treatment
Grade 1: In this level, medications are prescribed by the vet to reduce pain and inflammation, support the production of joint fluid and enable the cartilage to heal.
Grade 2: Similar to Grade 1 where the necessary medications need to be followed. Surgical treatment might be undertaken by the vet.
Grade 3 and 4: Both these stages are acute where the vet will definitely do surgery on the affected dog.
4. Hip Dysplasia
Symptoms
- Lethargy
- Anxiety
- The decrease in the amount of normal daily activities
- Limited range of body movement
- Difficulty to rise or stand up from the laid position on the ground
- Avoidance of usual activities like running, jumping and climbing stairs
- Disabled rear leg
- Stand with both the legs so close to each other
- Gait walk
- Looseness in the joints
- Grating in the joints during walking
- Bulged shoulder muscles that form due to heavy pressure applied to the front leg while walking and managing the handicapped rear leg
Causes
- Genetic problem
- Malnutrition
- Trauma or Injury
- Heavy exercising or lack of exercise
- Excess weight gain and obesity
Treatment
The veterinarian will determine the treatment for a dog with hip dysplasia after having a close observation or examination of the stage of the disease. The treatment methods could be:
Dietary management – A diet that is low in protein and fat are usually recommended by a vet for the affected dog. The heavyweight gain will further weaken the dog’s hips.
Physiotherapy – The vet will recommend soft exercises for the dog so that its joints do not face the risk of breakage. Likewise, they will also advise the owner to not give exercise/s to the affected dog on a hard surface.
Medications – NSAIDs (non-steroidal and anti-inflammatory drugs) will be prescribed for the affected dog so as to reduce its pain and inflammation. Opioids is an oral medication that is normally recommended.
Some chondroprotective supplements like chondroitin sulfate, glucosamine, Vitamin C, Omega 3 and 6 fatty acids and hyaluronan are given to hip dysplasia dogs.
The purpose of these supplements is to preserve and lubricate the cartilage in the joints of the affected dog.
Surgery
A veterinary surgeon could adopt either of the following surgeries on a dog with hip dysplasia:
- Triple pelvic osteotomy (TPO) – The surgery is usually done on infant dogs (less than 1 year of age). The surgical procedure involves the selective cutting of the pelvis in three different places.
The successful result of this surgery is notable through the smooth rotation of the pelvic socket that will cover the head of the femur. - Excision Arthroplasty – The surgery involves the excision (removal) of the femoral head and neck. Thereafter, the dog will not feel that mysterious pain faced earlier because of no bony contact between the femur and the pelvis.
- Total hip replacement (THR) – A widely applied surgical treatment method by veterinarian surgeons for treating dogs with severe hip dysplasia.
The hip joint of the affected dog will be replaced with an artificial hip. The dog will not suffer any pain or other inconveniences that it experienced prior to the surgery.
5. Ear infections
Symptoms
- Head Shaking
- Scratching and rubbing the ears
- Reddish ears
- Inflammation
- Discharge of yellow or black substance from the ears
- Odor
- Swelling
- Hair loss
- Circled walk
- Unsteadiness in the walk
- Hearing Loss
Causes
There are different types of ear infections with each having its own cause. The causes of ear infection in dogs constitute:
- Anatomy of a dog like its long floppy ears provides ample space for a build-up of bacteria and yeast in the middle, inner and outer ears
- Accumulation of wax in the ears
- Entry of some foreign substances into the ear
- Hypothyroidism
- Severe head injury due to an accident
- After swimming or bathing, a dog will automatically create a moist environment in its ears and this is sufficient for yeast and bacteria to enter
- Transmission of bacteria to the dog’s ears through an infected mite’s bite
- Presence of tumors in the ear canal
Treatment
Depending on the type and cause of the ear infection in a dog, the veterinarian will give the relevant treatment. Normally, the vets begin treatment by prescribing anti-bacterial, anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial drugs for a dog with the ear infection. Vets may also check if the dog suffers from cauliflower ears.
Topical ointments and solutions are the next steps. In cases of dogs facing severe or frequent ear infection, the surgical method will be adopted by a veterinarian. All the blocks in an affected dog’s ears will be cleared.
Whatever be the case, a dog owner must ensure that they visit the vet for a consultation if the dog is affected by the ear infection. The nature of treatment could be any type of solution, ointment or medications that could also include organic type.
Some related professionals recommend the combination of holistic treatment and traditional medicine for treating a dog’s ear infection. Traditional medicines like steroids such as Prednisone will break the cycle of infections which can then be followed by a holistic approach.
The holistic method involves the observation of the diet, lifestyle and general health of the affected dog.
Cocker Spaniel Price
In the US market, the average price of a Cocker Spaniel is somewhere at or between the price tag of $600 to $800. Various factors determine the price of the dog such as its age, parents, bloodline, overall health, vaccination details, and quality of breeder.
However, it is found that English Cocker Spaniel dogs can be purchased at a price range of $900 and $1200. In the UK, the average purchase price of a Cocker Spaniel is in the range of £600-£800. Non- kennel club registered dogs will be gettable at even a lower price of $500.
Cocker Spaniel Breeders
Cocker Spaniel Breeders in the USA
- Myrdin Cocker Spaniels
Address: Cornwall, New York (NY)
Tel.: 845-534-3724
E-mail: myrdincockers@verizon.net - Pinecliff Cockers
Address: West Mulford, New Jersey (NJ)
Tel.: 973-277-1434
E-mail: lisa@pinecliffcockers.com - Bella Notte Cockers
Address: 12270 Schulz Rd,
Herald, CA 95638
Tel.: 1-916-613-3270
Cocker Spaniel Breeders in the UK
- Kellys Kennels
Address: Brookside Farm, WA3 7AY
Tel.: 07807047619
E-mail: info@kellyskennels.co.uk - Eastriding Spaniels
Address: East Riding of Yorkshire, Bridlington
Tel.: 01262 851000
E-mail: kelly.jenkinson@hotmail.co.uk